Bonanza Offer FLAT 20% off & $20 sign up bonus Order Now
Question:
Chadstone is one of the prestigious shopping malls with diversified businesses under one roof. Since its inception in 1960's, Chadstone has undergone a series of developments. However, to maintain its enormous customer base, the enterprise aims at adding value to development projects ranging from an additional car park, and new public transport facilities. Specifically, development proposals include; hotel accommodation, other offices, new leisure and entertainment grounds, dining precinct, and digitalized cinema hall (Hacking and Company, 2012, p.87).With the stated project proposals, it is relevant that the European Construction Company familiarizes with Australian legal framework and standards, areas and sources of law, environmental assessment and sustainability initiatives, and the professional codes of building and construction in Australia to win the construction tender.
Australian legal framework on building and construction is defined by some laws primarily adapted from universal laws of the state. These rules strategically aim at enhancing quality work, relationship bonds between constructors and project owners and boost safety standards for people and workers during project completion process. Relevant laws to building and construction in Australia include; contract law, the law of tort, and breach of statutory duty (Clark and Griggs, 2015, p. 161).
The law mainly governs agreements between the contractors, construction engineers, forepersons and the hiring party. Contract law is largely determined by five essential elements that bind contract formation (McKendrick, 2011, P. 53).These are agreement, consideration, capacity to enter legal relations, an intention of entrance into the settlement and certainty.
Agreement. The agreement is analyzed through rules of the offer provided by the hiring party and the acceptance by the Construction Company or particular contractor. Expressively, the agreement is determined by the willingness to bind on profound terms and communication by the parties involved to strike a deal. In instances where the transaction is denied, further negotiations are spelled out. For example, an agreement will act as the inception stage of the association between the European Construction Company and the management of the Chadstone project giving each part a chance to spell out their terms and reach a concession for further proceedings of the project. For example expectations and design, the layout may be discussed as well as charges of construction allow consistency and efficiency in completion of the project.
Considerations. The bargaining part of the project regarding financial requirement, property, service provision, and the promise whether to take or reject the contract is this.
The capacity of entry. Ability to enter legal relations takes into considers issues related to age, sound mind, amongst others. Therefore the European Construction Company shall recruit construction engineers by skills and qualification to ensure similar project demands are met competitively.
The intention of entrance into the contract. Intentions are legal relations between the parties. They may either be private or non-commercial or commercialized in nature. Private or non-commercialized intentions may not be enforced whereas the commercialized ones must be applied since they are legal and binds the parties involved in completing the contract. Chadstone construction project involves a series of procedures and workflow patterns. Therefore, a commercialized intention will practically apply to ensure that the European Construction Company remains objective and works out the project to completion. The agreement is sealed by both parties through signing the documents. Signing the agreement equally ensures that the parties are dedicated to seeing the project succeed (Stone and Devenney, 2013, p. 210).
Certainty. Contact formation demands to ensure the agreement is clear and sufficient. Certainty binds the parties into the completion of the project at hand. Moreover, individual contracts save the parties from problems related to procedures, disagreement, and violation of promises made during the agreement
Partisan issues addressed by the law of tort revolve around civil wrongs against contractual obligations. The law confronts issues to do with property damage, personal injuries, and actions of contractors. Common torts in Australia include trespassing private property for example land, negligence due to breaching of statutory duties, public nuisance and interfering with judicial processes, intentional economic damage, and interference with family and employment relations (Cooke, 2007, P. 166)
Practically, being conversant with the issues addressed under this law, the European Construction Company shall formulate a working framework that takes into consideration safety measures of its employees. Injuries shall be mitigated while on call, satisfy all legal requirements as far as construction of Chadstone shopping center is concerned. Minimal wastage of resources, clear communication patterns, reduced public nuisance by observing environmental, development of compensation plan for families and workers sent on duty for long shall be witnessed. Elements of the boundary between Chadstone and its neighbors shall also be checked to evade land and space related conflicts, and determine the best insurance package suiting its demands.
Breach of statutory duty allows clients to recover their money in case the contract is forfeited as compensation for the damages caused. The law of negligence plays a part in instances where one party owes the duty of care to another. Breach of duty is manifested via injury caused, and the loss sustained. The duty of care arises by the decision to undertake a specified activity for example construction of a building. The law categorically limits the number of complainants due to a breach of duty. Duties may range from maintenance of a safe working place to professional standards of the work in question. Once it is established that the obligation exists, an evaluation test is done to determine the level of damage caused. Standard of care may be higher depending on the standard of individual professionalism and skills related to the job. Ideally, this law applies due to failure of conducting duties or fulfilling the obligations imposed by legislation (Stanton, 1986, p. 245).
Licenses and licenses are the integral part of government requirement as well as organizations. These define the business attributes of the firm. Therefore, the European Company will be able to prove its competitive business position within the market to Chadstone management for approval purposes. Ideally, licenses show that a building company or a contractor is certified by the legal bodies. Since Australian construction industries operate on the domestic or residential basis, the market is characterized by small contractors with limited liquidity. The state governs and regulates building work via licensing protocol to ensure quality; cost and balanced bargaining power are adhered to by all stakeholders (Schröder, 2015, p. 111). The following licensing requirements apply to Australian building companies. Registration as a builder before construction work, defining architects role for example plumbers, gas fitters, and electricians must prove their eligibility in service provision, stating the time frame within which a builder litigates with building disputes, and obligations relating to insurances.
The Commonwealth in cooperation with Australian government has effected legislation to regulate occupational health and safety of employees and the surroundings. Victoria and Western Australia have adopted health and security systems to ensure contractors consider the welfare of the communities within and other workers while performing their duties to limit risks such as injury of employees. For example, the helmet law.
Sample health and safety plan; helmate
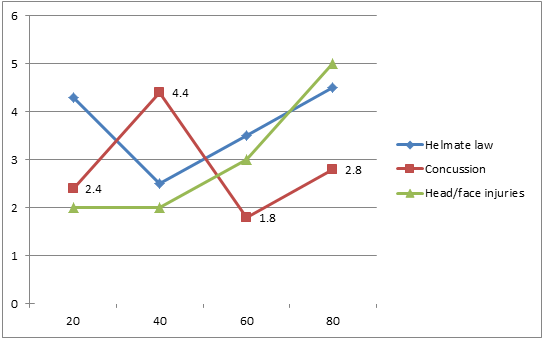
Sorce: Enserink, 2014, p. 1261
From the data, it can be noted that the number of head and face injuries reduced from 4.4- 3.4 with an increase of observing helmet law to prevent injuries.
The risk management approach to safety and authoritative codes of practice are score points during security initiation practices. This element will help the European Construction Company to initiate reasonable practices and duties to conduct itself in a manner that it limits hazards, familiarize with the risks and adopt ways of eliminating them, construct a financial docket in response to meeting costs of the risk. Failure in compliance with the risk management initiatives deems the company liable to criminal prosecution attracting fines or incarceration.
Major environmental issues affecting building and construction for sustainable development are water and waste disposal. The quality of water is maintained by observing state's act on pollution, and discharge to sewerages. These ensure terrestrial and aquatic living things are protected against extinction and infection. Legislation equally controls waste generation, transportation, and disposal. For instance, by observing the environment, the European Construction Company shall have a site waste management plan to manage waste throughout the project. The site will equally be used by Chadstone clients and staff after the construction work.
Matters regarding national environment such as energy efficient buildings are attracting government focus, investors, builders, and tenants. The concern has led to the development of green rating schemes in Australia. These are "The Green Star rating scheme operated by the Green Building Council of Australia (GBCA)", and "The National Australian Built Environment Rating System ." (Patrick and Kingsley, 2015, P. 289) .The green star assesses building and construction operations impact on the local community. The assessment is focused on the following building elements, indoor environment quality, materials, management patterns, energy use and emissions, site location, water usage, and innovation in process and design.
These are technical provisions that guide design, construction, and structures of buildings in Australia. Ideally, these systems were initiated under the Australia building act of 1975 and have undergone further amendments. The codes tackle a range of issues about industrial payments, fair work, code of practice, subcontractors, sustainable planning, safety and health, and gender equity (Glencross-Grant and Walker, 2003, p. 253).
The act covers all parties in construction chain to ensure they receive payment for the task undertaken. The Act applies to commercial construction contracts inclusive of supply of goods and services. The act resolves disputes of payment, stipulate payment timeframes and schedules. Some of the payment documents include tax invoice, payment claim form, and online adjudication application (WongPartnership and Singapore, 2004, p. 133).
The act puts in place workplace relations systems based on the safety of employees with minimal employment conditions. Employers are called upon to issue new hires with fair work information prior or after employment, for example, dismissal procedures. The Australian Fair Work Act commission works under the national workplace relations tribunal to carry out a range of functions such as wages and unfair dismissals disputes.
Code of practice measures building and construction industries intends to encourage best outcomes for projects and promote behavior changes in industries. Practically, this law defines ethical standards guarding behavior of all parties, outlines safety expectations maximize opportunities for local industries participation, encourages cooperation, and professionalism. The stated guidelines support proactive management of work relations, manages costs of productivity, enhances workplace safety and health, and improves innovation.
The act seeks to achieve development outcomes through managing processes, effects of development, and continuous coordination of the local and state planning initiatives.
Sample construction works planning
Sample health and safety plan; helmet
Source: Author, 2016
The act deals with controversies relating to permits, reinstates the power of trained health and safety representatives to direct workers limiting exposure to risks, seek assistance in case of hazards such as collapsing of an ongoing building, and charge a penalty on firms and persons forfeiting safety precautions.
The act focuses on ensuring both genders are treated on a similar scale by addressing issues such as equal remuneration and rights relating to family and care.
Concisely, Australian building and construction are defined by legislative standards ranging from contract law, law of tort, and breach of statutory duty. Additionally, the industry takes pride in the state laws, and health and safety need as elements constituting law. However, initiatives on assessment of the environment are put in place to help in planning and to put the system into practice. Further, it is important to note that Australia building and construction industry is guided by principles of conduct under various Acts such as Fair Work Act, Building and Construction Industry Payment Act, code of practice, Sustainable Planning Act, Workplace Gender Equity Act, and Workplace Health and Safety Act.
Clark, E., and Griggs, L. (2015) Commercial and economic law in Australia. Netherlands Kluwer Law International. Pp. 145-167
Cooke, J. (2007) Law of tort (foundation studies in law series). 8th ed. Harlow: Pearson Longman. Pp. 160-200
Enserink, M. (2014) ‘Hats off to Vietnam's helmet law', Science, 345(6202), pp. 1261–1261. doi: 10.1126/science.345.6202.1261.
Glencross-Grant, R., and Walker, P. (2003) ‘Survey of building sands in Australia', Construction and Building Materials, 17(4), pp. 259–268. doi: 10.1016/s0950-0618(02)00115-0.
Hacking, J., and Campany, D. (2012) Photography: The whole story. London: Thames & Hudson. Pp 69-100
McKendrick, E. (2011) Contract Law (Palgrave Macmillan Law Masters). 9th ed. Basingstoke: Palgrave Macmillan. Pp. 45-78
Schröder, M. (2015) ‘Property protection of public licenses and permits', China-EU Law Journal, 4(1), pp. 105–120. doi: 10.1007/s12689-014-0052-x
Stanton, K.M. (1986) Breach of statutory duty in tort. London: Sweet & Maxwell. PP. 243-250
Stone, R., and Devenney, J. (2013) The modern law of contract. 10th ed. London: Taylor & Francis. Pp. 156-278
Patrick, R. and Kingsley, J. (2015) ‘Exploring Australian health promotion and environmental sustainability initiatives', Health Promotion Journal of Australia, doi: 10.1071/he15008.Pp.234-300
WongPartnership and Singapore, A.W.P. (2004) Annotated guide to the building and construction industry security of payment act 2004. Singapore: Sweet & Maxwell Asia. Pp 77-110
MyAssignmenthelp.co.uk takes pride in announcing that thousands of students in UK have chosen us as the best assignment help provider. The main reason behind overwhelming popularity of our assignment writing services is we understand students’ needs and fulfill them in the best possible manner. Students, taking up our assignment writing help, are guaranteed to get top-notch quality content, on-time delivery of the paper and expertly written plagiarism-free assignments in their accounts.
Upload your Assignment and improve Your Grade
Boost Grades