Bonanza Offer FLAT 20% off & $20 sign up bonus Order Now
Internet of Things (IoT) is one of the most attractive and essential aspect in the technological world. The concept of Internet of Things is mainly used for the situations where the physical world is controlled by the sensors (Xia et al., 2012). Among the last few decades the application of Internet of Things dominated the physical devices by the software support and network connectivity. Aerial healthcare is one of the small scale organizations within Melbourne. The headquarters of the organization is situated in Melbourne. The main objective of the organization is to provide the service to people who need it but cannot afford it for financial issues. The projects organized by Aerial healthcare are for serving the Australian as well as the people coming into the country. There are total 2000 people got employed within this organization in several sectors. Aerial healthcare expanded their business among other countries also; it has 20 donor countries with them for providing the financial and other necessary support to them. These donor countries have their own head quarters in Melbourne individually. 40% of the total funds are collected from their foreign investors, so it can be said that the organization has developed their business globally. The total project and administration cost are mainly funded by these foreign parties. The donor countries also have systems located within their head quarters, which is internally connected through the internet to Melbourne.
This report is presenting the impact of Internet of Things on healthcare industry with respect to the Aerial healthcare.
Introduction: This part of the report is providing the background of the Aerial healthcare and objectives of this report.
Discussion on Internet of Things: This part is providing the application currently Aerial healthcare is using and the application they want to be implemented within their organization. in addition to this, this part of the report is elaborating the advantage, disadvantage, ethical, social and legal impact of Internet of Things on healthcare industry.
Conclusion and recommendations: This conclusion part of the report is elaborating the findings collected from the research. The recommendations are providing the concerned perspective to the CEO of Aerial healthcare.
The evolution of the internet can be classified in to four stages. These stages are as follows:
Stage1: ARPANET
This stands for the Advanced Research Project Agency Network (Gubbi et al., 2013). This project was introduced to the technological world for the research and academic purpose. This was started by US military and defense department.
Stage 2: The Globe Rush for Domain Names
In this time of the technological era HTML was developed and the whole technical industry was rushing behind the domain names (Perera et al., 2014). The objective behind this was to make their products and services more popular all over the globe.
Stage 3: the boom and bust of the dot com bubble
The migration of the internet has done from the static phase to transactional phase. E-business was developed in this era.
Stage 4: Social Experience Web
The social interaction has become so easy because of the utilization of the internet. Facebook, Groupon and Twitter have enabled the system for making interaction with individuals all over the world (Miorandi et al., 2012).
Stage 5: Internet of things
This was an immense development in the technological world, which changed the life of the people and their work culture. The Internet of Things is described as the connections between the objects used every day. Internet of things maintains a collaborative relationship among these objects (Turner et al., 2014).
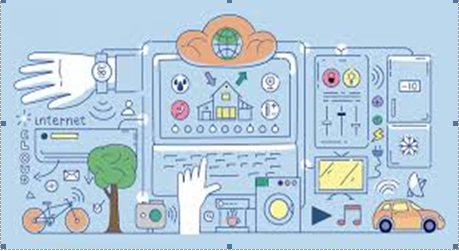
Figure 1: Internet of Things
(Source: Perera et al., 2014, pp- 450)
History of Internet of things: Internet of Things was developed by Kevin Ashton in 1999. According to the RFID, the internet of things is the globally defined network which connects the objects; those are individually addressable accordingly standard communication protocol. Control systems, embedded systems, and many other traditional fields are incorporated among Internet of things to specify the inter device communication through the internet. This aspect was first used in the Auto ID centre at MIT (Zanella et al., 2014). Radio frequency identification is identified as the pre- obligatory for any system. This can be utilized in the personal as well business sector. Here the healthcare industry is chosen for reviewing the usages of Internet of Things in personal domain.
The reliance on Internet of Things is increasing day by day as the technology is meeting all the demands of the consumers. Aerial healthcare is utilizing Internet of Things through clinical care and remote monitoring.
Clinical care
There are Internet of Things driven non-persistent monitoring system for the patients, those who requires the attention of others as they are not physiologically stable. The system employs sensors for gathering the physiological data (Perera et al., 2014). These data are stored and analyzed using the gateways and cloud. These informative data are forwarded to the considered individuals and further analysis is done on those data and information.
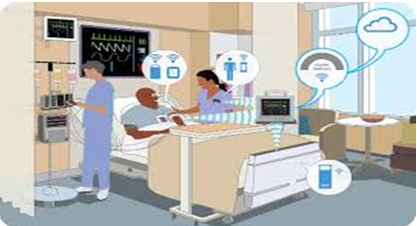
Figure 2: Clinical care
(Source: Whitmore et al., 2015, pp- 270)
There may be caused many health risks only because of the lack of immediate access to the health monitoring systems. This was one of the most important issues the Aerial healthcare was facing. The Aerial healthcare utilized efficient wireless elements connected through Internet of Things for gathering the information about the incidents those are taking place (Barnaghi et al., 2012). There are several algorithms and sensor or devices which do help this monitoring system.
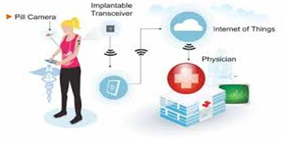
Figure 3: Remote monitoring
(Source: Zanella et al., 2014, pp- 30)
Devices for making connection with Internet of Things:
There are mainly four connective networks which connects the Internet of Things with different devices: WSN, standard user interfaces and displays and connectivity of the network for accessing infrastructural services. WSNs connect the sensors and actuators (He & Zeadally, 2015). It has extension USN, which is an application system connected with Internet of Things. These systems operated in both independent and hybrid networks network.
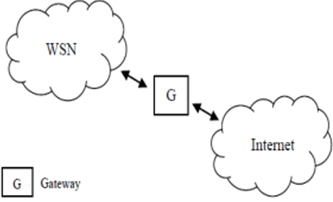
Figure 4: Independent network
(Source: Stankovic, 2014, pp- 5)
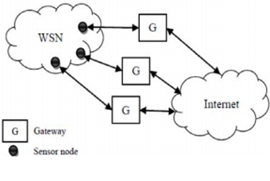
Figure 5: Hybrid network
(Source: Granados et al., 2014, pp- 280)
There are several applications that can be implemented in Aerial healthcare, among these all applications two are chosen for implementing in the organization. These applications are explained below:
Monitoring the aged families: Aerial healthcare can use the sensor based monitoring system for recognizing the senior residents who are unable to do their own work or facing some medical emergency. This sensor tracks the residents while utilizing the battery operated alarming system (Whitmore et al., 2015). This system is totally cost effective according to the demands of the Aerial healthcare. In addition to this, the installation procedure of this device is easier than any other system. It only needs a wide area for communicating interface. The elementary device which will make the doctors or nurses aware of the situations may be designed as per the convenience, such as it may be waterproof sensor systems. These systems are designed as per required time span. The timer incorporated within it can be set at 10 to 15 minutes of interval. The timer is added for signaling the ultrasound receiver. The receiver communicates with the end user through the WLAN (Stankovic, 2014). The whole continuous analysis of the system is done through the gateway or cloud. The data relevant to the system is broadcasted through the wireless wide area network. This aspect helps the end user to detect the emergency event.
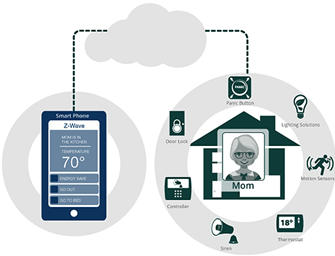
Figure 6: monitoring of senior person
(Source: Domingo, 2012, pp- 590)
Controlling, scalable heart monitoring system: Another application that can be utilized within the Aerial healthcare is the heart rate monitoring system that is continuous and scalable. The organization may set a particular threshold for the individual patient (Want et al., 2015). These threshold limits differentiate the specific parameters of the individual patients, which defines their condition. These parameters are: heart rate according to the ECG, rate of the respiration, level of the activity, position of the body. There are several vital signs that should be monitored according to the physical demands of every individual. These signs are: blood pressure, level of the cholesterol etc. All of these aspects specify the functionality of the heart. This rhythmic monitoring system defines the effectiveness of the heart (Granados et al., 2014).
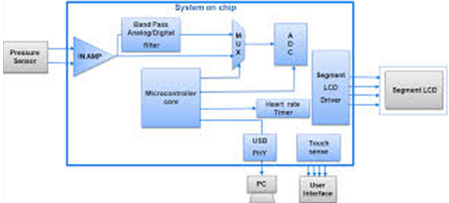
Figure 7: Heart monitoring system
(Source: Kang et al., 2014, pp- 1520)
There are several advantages and disadvantages of Internet of Things in healthcare industry. These advantages and disadvantages are described here on the basis of the Aerial healthcare.
Short- term care planning: Transitional stage between the chronic illness and the recovered stage are very much crucial for every patient. This ensures the chances of recovery for the patients. PGD shows the future guidelines for the betterment o the patients, which was previously provided by the handwritten notes by the doctors (Domingo, 2012). This aspect made the treatment easier than the conventional ways of treating the patients.
Home care and management of chronic diseases: In case of the home management and chronic disease management PGD provides the proper solution through the use of Internet of Things. The sensors are used with Internet of Things for measuring the conditions of the patients (Ning et al., 2013).
Population based evidences: PGD also help the he end users of Internet of Things to determine the population controlling measures (Chen et al., 2014). This determination introduces the risk analysis and provides the solutions for the betterment of the situations.
Utilization of PGD in proper place: PGD provides a range of clinical help to the end users of the Internet of Things, though there are no specifications for the proper implementation area. Most of the organizations face so many challenges during the implementations of the new technologies in within the conventional system (Kang et al., 2014).
Reluctance regarding the clinical issues: The reluctant nature of the end user in Internet of Things introduces the changes in paradigms used for taking care of the patient. PGD needs the adjustment to the clinical workflow and compensation model for clinicians.
Privacy and security limitations of data: The increased number of the Internet of Things enabled devices and systems which are sharing their data through common network. This aspect increases the chances of data theft and vulnerabilities (López et al., 2012). The privacy and data security is hampered due to these aspects.
Arial healthcare have decided to introduce two applications of Internet of Things Heart rate monitoring system and monitoring system for the aged people. The following impacts are discussed with respect to these two aspects.
Ethical impact Internet of Things (IoT)applications: According to the above mentioned applications chosen by the Aerial healthcare, it is the duty of the management of the organization to check if the ethical aspect is maintained or not. The patients with critical situations are being provided help through Internet of Things applications, so if the speed of the internet goes down it will be harmful for those patients (Guo et al., 2013). Except these, the detection of vulnerabilities within the system may harm the patients from various perspectives. Data theft, hacking etc are the specific examples of these vulnerabilities.
Legal impact of Internet of Things applications: The above mentioned two applications of Internet of Things are designed according to the laws and regulations provided by the government of Melbourne. The data used for the Internet of Things applications are always follow the anti- discrimination rules and fairness. The data security is maintained. The data collected from each patient are totally secured and safe within the records for the authority. These data are only provided to their family members. This application follows Fair Housing Act, which states that the data should be protected any external malware (McEwen & Cassimally, 2013). Legal issues are concerned when the rules and regulation set by any country is not maintained or violated. Internet of Things is having intense impact on the technological world, which is changing the meaning the of life. If the consideration is about the healthcare industry then the legal aspect is very crucial to be analyzed. The regulation provides guidance to the patients as well as the doctors.
Social impact of Internet of Things applications: Internets of Things also have societal impact like other technological advancements. The two applications, which the Aerial healthcare wants to introduce in their system, make the communication easier from the end of the patients (Wu et al, 2014). The monitoring process of the patients ensures the ready action to be taken for them, as there are so many critical situations where the doctors have to respond quickly, so this system helps to provide correct action. Internet of Things is becoming realistic day by day. Previously the Internet of Things was not that much popular and the infrastructure was not able to incorporate this system (Elkhodr et al., 2013). The healthcare industry got the effective benefit of the technological development. Aerial healthcare will be able to operate many critical situations by using two new monitoring systems for aged people and for heart rate. Society is getting the benefit from these applications of Internet of Things.
Internet of Things is nothing but the technological advancement of modern era. In addition to this, Internet of Things is the combined result of the application of electronics, computer networking, and interconnection between these networks. The large scale impacts of the Internet of Things have transformed the human life. This report is discussing the impact of Internet of Things in the healthcare industry. Here the healthcare organization chosen for the implementation of Internet of Things is Aerial healthcare. Aerial healthcare is considering two main application of Internet of Things to be implemented within their organization. Technical descriptions of these applications are elaborated with their proper advantages in the healthcare sector. Internet of Things uses WSNs and USNs as the devices for setting up interconnection between the patents and gadgets the doctor or nurses are using. The ethical, legal and social impacts are highlighted with respect to the present scenario of the Aerial healthcare. Ethical impacts of Internet of Things are considered with respect to the security and safety measures for the end users. Social and legal impacts are focusing on the benefits the end users getting from the system. The recommendation provides the positive impacts of these applications on Aerial healthcare. The report is making the facts clear that the impact of Internet of Things is getting revolutionized in the healthcare industry. This revolution specifies the affordable and accessible car for the patients. The recommendations provided in this report to put more focus on the importance of these applications of Internet of Things.
Personalized healthcare facilities can be incorporated anywhere at any time with the help of the Internet of Things. Internet of Things have been revolutionized the monitoring process of patients. Aerial healthcare want to implement two applications of Internet of Things for monitoring their patients: heart rate monitoring system and monitoring system for the aged people. The following recommendations are providing the beneficial perspective of the Internet of things to the CEO and higher authority of the Aerial healthcare:
Monitoring system of heart rate: Heart rate is one of the important aspects to be measured for every patient. The alarming system incorporated within this make the nurse or doctor aware of the conditions of their patients. Generally 15 to 20 seconds of gap is considered for the interval. The data collected from this system is utilized for the measuring other specific changes within the human body, such as: blood pressure, temperature of the body, cholesterol level etc. Heart is considered as the crucial part of the human body, so the care of it should be taken delicately. Aerial healthcare should maintain a p[roper database to ensure the records of the data collected from the concerned monitoring system, this will also maintain the ethical aspect with respect to the consumers.
Monitoring process of the aged families: This is another technological advancement, which the Aerial healthcare wants to incorporate within their system. Every healthcare organization have their special care unit for monitoring the aged people separately, as in most of the cases they are unable to take care of themselves. Uses of Internet of Things have made it possible to monitor the aged people easily. This monitoring system introduces a proper alarming system for the old people, with the help of which they can easily inform the doctor or nurses about their conditions and needs. There are several cases of negligence in the emergency situation. This technological advancement introduces a new system to provide proper care to the aged people when they need it badly.
The above mentioned recommendation to the CEO of Aerial healthcare provides an overview of the impact of these technological advancements.
Barnaghi, P., Wang, W., Henson, C., & Taylor, K. (2012). Semantics for the Internet of Things: early progress and back to the future. International Journal on Semantic Web and Information Systems (IJSWIS), 8(1), 1-21.
Chen, Y., Han, F., Yang, Y. H., Ma, H., Han, Y., Jiang, C., ... & Liu, K. R. (2014). Time-reversal wireless paradigm for green internet of things: An overview. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 1(1), 81-98.
Domingo, M. C. (2012). An overview of the Internet of Things for people with disabilities. Journal of Network and Computer Applications, 35(2), 584-596.
Drucker, P. F. (2015). Internet of Things.
Elkhodr, M., Shahrestani, S., & Cheung, H. (2013, April). The Internet of Things: Vision & Challenges. In TENCON Spring Conference, 2013 IEEE(pp. 218-222). IEEE.
Granados, J., Rahmani, A. M., Nikander, P., Liljeberg, P., & Tenhunen, H. (2014, November). Towards energy-efficient HealthCare: An Internet-of-Things architecture using intelligent gateways. In Wireless Mobile Communication and Healthcare (Mobihealth), 2014 EAI 4th International Conference on (pp. 279-282). IEEE.
Gubbi, J., Buyya, R., Marusic, S., & Palaniswami, M. (2013). Internet of Things (IoT): A vision, architectural elements, and future directions. Future Generation Computer Systems, 29(7), 1645-1660.
Guo, B., Zhang, D., Yu, Z., Liang, Y., Wang, Z., & Zhou, X. (2013). From the internet of things to embedded intelligence. World Wide Web, 16(4), 399-420.
He, D., & Zeadally, S. (2015). An analysis of RFID authentication schemes for internet of things in healthcare environment using elliptic curve cryptography. IEEE internet of things journal, 2(1), 72-83.
Kang, K., Pang, Z., Da Xu, L., Ma, L., & Wang, C. (2014). An interactive trust model for application market of the internet of things. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 10(2), 1516-1526.
López, T. S., Ranasinghe, D. C., Harrison, M., & McFarlane, D. (2012). Adding sense to the Internet of Things. Personal and Ubiquitous Computing,16(3), 291-308.
McEwen, A., & Cassimally, H. (2013). Designing the internet of things. John Wiley & Sons.
Miorandi, D., Sicari, S., De Pellegrini, F., & Chlamtac, I. (2012). Internet of things: Vision, applications and research challenges. Ad Hoc Networks,10(7), 1497-1516.
Ning, H., Liu, H., & Yang, L. T. (2013). Cyberentity security in the Internet of Things. Computer, (4), 46-53.
Perera, C., Zaslavsky, A., Christen, P., & Georgakopoulos, D. (2014). Context aware computing for the internet of things: A survey. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 16(1), 414-454.
Perera, C., Zaslavsky, A., Christen, P., & Georgakopoulos, D. (2014). Context aware computing for the internet of things: A survey. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 16(1), 414-454.
Skarmeta, A., & Moreno, M. V. (2013, August). Internet of things. InWorkshop on Secure Data Management (pp. 48-53). Springer International Publishing.
Stankovic, J. A. (2014). Research directions for the internet of things. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 1(1), 3-9.
Turner, V., Gantz, J. F., Reinsel, D., & Minton, S. (2014). The digital universe of opportunities: rich data and the increasing value of the internet of things. IDC Analyze the Future.
Want, R., Schilit, B. N., & Jenson, S. (2015). Enabling the Internet of Things. IEEE Computer, 48(1), 28-35.
Whitmore, A., Agarwal, A., & Da Xu, L. (2015). The Internet of Things—A survey of topics and trends. Information Systems Frontiers, 17(2), 261-274.
Wu, Q., Ding, G., Xu, Y., Feng, S., Du, Z., Wang, J., & Long, K. (2014). Cognitive internet of things: a new paradigm beyond connection. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 1(2), 129-143.
Xia, F., Yang, L. T., Wang, L., & Vinel, A. (2012). Internet of things.International Journal of Communication Systems, 25(9), 1101.
Zanella, A., Bui, N., Castellani, A., Vangelista, L., & Zorzi, M. (2014). Internet of things for smart cities. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 1(1), 22-32.
Upload your Assignment and improve Your Grade
Boost Grades