Bonanza Offer FLAT 20% off & $20 sign up bonus Order Now
Question:
Answer:
Introduction
Management and sustainability are the key areas that seldom walk parallel, the issue with the two of these is the relation of management with profit making and sustainability is an altruistic principle. Nevertheless there are certain companies that are epitome of both high moral ground principles of management and sustainability. IKEA is an example in this context. IKEA took up the issue of sustainability with its furniture business and continued it further with its cotton business where it took the sustainability product scorecard to include the producers in this case the farmers.

IKEA Store in California. Source: IKEA.com
In today’s business scenario stakeholders are the most important piece of the business puzzle. These stakeholders effect the effective running of the business either directly or indirectly, they are thus a huge resource for the company. These days the power distance equation for these stakeholders have been altered at varying levels, thus there are diverse levels of power and usefulness to every company. Likewise the stakeholders have been divided into four categories these are highly interested, highly powered the contrast being of low interest and low power. These stakeholders move the dynamics of the companies very differently thus there are specific strategies to manage each of these patrons. Needless to mention the key investors and stakeholders who have the high relative power and interest are much more noteworthy than the ones which are in the low category. Then we should look at the role of managers who interact with these players in order to achieve higher profits and above all sustainability for the organization. Thus business managers pay most attention to the stakeholders in the higher category since they are the most relevant customers who help in generating profits.
Moving onto the aspect of why the concern about key stakeholders is so crucial for a business. Stakeholders keep the firm running healthy in other words they keep it flourishing, accurately. The key goal of a running business is to generate profits and it is a no prize answer that whether the possibility of making profits let alone sustainability is possible without a strong understanding of the stakeholders. Stakeholders consists of clients, suppliers and vendors. They also include the workers, employees and managers. If the stakeholders are not effectively dealt with the business shall never survive (Mignouna, Ikea, Thottapilly and Ng 1998).
There are also concerns whether a bad corporate ethos shall be formed in case these stakeholders are not satisfied. This is an important case to be concerned with since businesses aren’t going to survive without the external outlook. It is therefore a myth that business I just run within a company and there externalities do not concern it. There are several other factors that concern a company and help in making it successful (Verbeke 2013).
Now we should look in the context of IKEA, this company is primarily a furniture company. The executives of this company claim that they have prospered and learnt about the business through their interaction with key stakeholders and partners. They have co-operated with a lot of trade unions and organizations through their experiences and consummated a lot more than they would have done had they done the same things all alone. They have shared and learnt from each other’s experiences. Let us look at it with the example of IKEAs trade agreement with BWI. BWI is the global union of more than 15 million members in close to 380 trade unions that spans the entire world and caters to the construction, timber and forestry industry. Both these units have a long term understanding and collaboration as per the IKEA code of purchase and conduct since the late 1990s. They have taken into account the purchase philosophy of the IKEA way of home furnishing. There is another organization called BSR, this company deals with material, tools, training and advisory services so as to ensure that IKEA’s philosophy of corporate social responsibility is part of its sustainability strategy. IKEA is a member of the BSR and a board member in IKEA is from BSR. The above examples relate to IKEAs learnings from collaboration with key stakeholders. This has helped IKEA to grow in a constructive manner all these years (Miles, Snow, Meyer and Coleman 1978).
This has led to a complete focus on the “4 O’s”, this is related to the external environment, the organization, employees and oneself.
These classifications have played a significant part for organizations like IKEA in a way, this has also generated métier not only from themselves, but from other organizations, to make these four factors a benefit to the company.
We will perform the industry analysis for IKEA by using the Porter’s five forces framework.
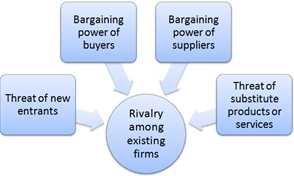
Porter’s 5 Forces Analysis; Source: HBR
Threat of new entrants in case of the furniture industry is quite significant even though these industries are capital intensive without major regulatory barriers. IKEA also operates in the home appliances industry and there too this threat is significant. There are no legal restrictions as well as trade barriers in place (Yip 2004). The industry knowledge barrier is also insignificant. But IKEA being an established player enjoys a certain level of economies of scope and scale. This is especially true for the initial phases of operation. There are considerable advantages that IKEA has over new entrants when we look at the coverage of channels that these companies will certainly lack in the initial years of operation. Hence though the barriers to entry are insignificant yet the cost leadership for new companies is quite significant and hence the threat is low to moderate (Konik-Rose, Wang, Larroque, Ikea and McMaugh 2007).
Bargaining power of buyers in this case the customers is enormous. The customers in this category are extremely price sensitive, thus IKEA must have a cost advantage over others. There are a number of local and global retailers from where customers can buy furniture. There are also insignificant switching costs and hence this absence makes the bargaining power of consumers very high.
Bargaining power of suppliers is frail. IKEA deals with more than 1200 suppliers in more than 50 countries, hence the lack of disparity between these supplies is very low and so plummets their bargaining power. IKEA also imposes a number of CSR programs on these suppliers due to a higher bargaining power and it also purchases products at low prices. An example is the reduction in energy efficiency by key suppliers by 20% in FY 2014. This figure was alarming in the year 2010.
Threat of substitute in case of IKEA products and services is comparatively low as not enough products that can switch the demand for furniture into some other new product. Also IKEAs model and range of products helps in keeping such substitutes at a distance.
Rivalry among existing firms is much greater than can be anticipated in the furniture market, there are a number of international players that operate at almost the same scale as IKEA, these are Galiform , Argos, Wal-Mart, , Euromarket Designs and others with these IKEA also has to beat certain big local players. However, currently IKEA is the acknowledged market leader in the industry of cut-price furniture in the global scale (Normann and Ramirez 1998).
Resources refer to the initiatives and processes that lead to a profitable utilization of the company’s asset base. This is created both within and outside the organization, though resources that are created within an organization are far more tangible. They are thus termed internal resources and are organization specific. These resources when contrasted with the externally obtained resources are termed organization addressable resources or external resources (Normann and Ramirez 1998).
Further, the resources that are catered to exceptionally specialized purposes, only and also being noteworthy to the firm by adding value to their goods and services are termed specific resources.

About Company. Source: IKEA.com
When we look at capabilities these are the critical resources that lead to s sustainable competitive advantage, thus they are termed distinctive in nature. If these capabilities are developed from an existing attribute that other organizations lack then they are termed distinctive capabilities. They must also be sustainable and appropriable for being considered distinctive.
We will understand IKEA’s resources and capabilities using the SWOT analysis framework.

IKEA: SWOT Analysis
IKEA understands its customer base much better than its competitors they have the advantage of understanding them extensively. They have made changes in their best practices statements and aligned their goals according to the purchasing factors that influence customers to buy a range of products. Low price is another keystone that they have included in their business model. Thus they have both efficiency and cost leadership with respect to their competitors. They have always worked in sustenance with the environment and innovated in a number of ways to keep costs lower and work in tandem with the environment.
This organization has been criticized several times for issues like improper treatment of employees and some advertising practices that are dubious. They have also been criticized by some sections of the media for lobbying with governmental authorities. This has led to certain negative publicity, hence they introduced their sustainability plan of action keeping farmers in mind.
IKEA recently has faced challenges in keeping the cost lower and maintaining the product quality high as before. There are certain consumer insight reports that indicate that an increasing number of customers are dissatisfied with their IKEA purchases. Most of them being so due to the quality of the products at the stores (Normann and Ramirez 1998).
Online channels is growing at a much faster pace than anticipated, IKEA can enter this space and can extensively look at how they can grow exponentially. When we look at retail markets they have grown close to 6% on average in developing economies in the last couple of years, this is an untapped market that IKEA can expand into and register growth in top-line
The firm operates in majority of the developed economies but hasn’t firmly stepped into developing economies, except China. There are a number of good options for the firm to establish a foothold and presence in Indonesia and Malaysia. They can also look at expanding in the South American emerging economies like Brazil.
As already mentioned there are a large number of low cost retailers in the market. The prevalence of online retailers has further marred IKEAs cost leadership strategy execution. These retailers also enjoy the same strengths as IKEA, which are low cost, high consumer base and market coverage.
There are a number of low cost retailers like Walmart and Tesco that have entered the homeware specialists market where IKEA operates.
Porter’s Generic Strategy Model
IKEA strives towards a world where kids in poverty stricken situations have enough prospects in order to ensure a better future for their kin.
IKEA wants to create a strong change by aiding and providing capital in some of world’s humblest economies. These geographies are funded by their well-rounded and long-term initiatives that would cater to issues among children like homelessness, poor wellbeing conditions, basic education and a sustained income.
As far as their 2014 records indicate Ikea has donated more than €105 million, this has generated support for children across 46 countries, and this has been possible due to their initiatives run by their 42 vendors and partners. They have also raised more than €11 million for UNICEF’s Save the Children campaign (UNICEF, 2014).
Conclusion
When we look at the sustainability report of IKEA, Sustainability Strategy for 2020 they suggest an achievement of sourcing all IKEA products specifically cotton from sustainable sources. They are also looking at researching for a product that could replace cotton and provide same properties to the consumers (Andrews and Roland 1987).
IKEA wants to create a strong change by aiding and providing capital in some of world’s humblest economies. IKEA strives towards a world where kids in poverty stricken situations have enough prospects in order to ensure a better future for their kin.
IKEA also imposes a number of CSR programs on these suppliers due to a higher bargaining power and it also purchases products at low prices. An example is the reduction in energy efficiency by key suppliers by 20% in FY 2014.
Thus IKEA has played the role of sustainable strategy champion in the furniture industry.
References
Butow, B.J., Gale, K.R., Ikea, J., Juhasz, A., Bedö, Z., Tamas, L. and Gianibelli, M.C., 2004. “Dissemination of the highly expressed”. Theoretical and Applied Genetics, 109(7), pp.1525-1535.
Marchand, D.A., Kettinger, W. and Rollins, J.D., 2001. Making the invisible visible: How companies win with the right information, people, and IT. John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
Mignouna, H.D., Ikea, J., Thottapilly, G. and Ng, N.Q., 1998. “Genetic diversity in cowpea as revealed by random amplified polymorphic”. Journal of Genetics & Breeding (Italy).
Strategy, A.E., 1998. “Design by directed evolution”. Acc. Chem. Res, 31, p.125r131.
Normann, R. and Ramirez, R., 1998. Designing interactive strategy: From value chain to value constellation. John Wiley & Sons.
Verbeke, A., 2013. International business strategy. Cambridge University Press.
Marchand, D.A., Kettinger, W. and Rollins, J.D., 2001. Making the invisible visible: How companies win with the right information, people, and IT. John Wiley & Sons, Inc..
Andrews, K.R. and Roland, C., 1987. About strategy. We can’t solve problems by using the same kind of thinking we used when we created them., p.150.
Miles, R.E., Snow, C.C., Meyer, A.D. and Coleman, H.J., 1978. Organizational strategy, structure, and process. Academy of management review, 3(3), pp.546-562.
Yip, G.S., 2004. Using strategy to change your business model. Business strategy review, 15(2), pp.17-24.
MyAssignmenthelp.co.ukassignment writing services that students trust. We offer our assignment writing services for a wide variety of assignment including essay help, dissertation help, case studies and more. Students can place their order with us anytime as we function 24x7, and get their copies at unbeatable prices. We guarantee that all of our solutions are plagiarism-free.
Upload your Assignment and improve Your Grade
Boost Grades