Bonanza Offer FLAT 20% off & $20 sign up bonus Order Now
The purpose of this situation analysis is to evaluate the marketing environment of clothing industry in Australia. In this situation analysis, the market competitiveness, producyt situation, distribution situation and environmental factors have been analyzed. This situation analysis examines the clothing market in Australia and addresses the relevant marketing environment factors related to the position of Pacific Brands in the Australian clothing industry. This analysis consist evaluation of PESTLE analysis, which helps to assess the uncontrollable external market forces.
Clothing sales in Australia has seen a phenomenal growth from the last decade. Previous researches revile that several new brands entering in the market. The target market of Pacific Brands is consumers who are aged between 25 and 50 years. Here the type of competition in the industry of clothing is monopolistic with different other brands who provide same kind of benefits. Pacific Brands has a target for differentiating itself from its competitors through creating a strong brand image.
Since its establishment in the year 1893 at Melbourne, Australia, Pacific Brands has undergone through a significant growth. The company is currently employing 3500 people who are dedicated in manufacturing and supply of socks, underwear, hosiery, baby wear, active wear and outwear (Pacificbrands.com.au, 2016). The company has achieved annual revenue of 789.7 million Australian Dollars in the year 2015. Its operating income was 64.2 million Australian Dollars in that particular year (Jagel et al., 2012).
Demand of the clothes starting from inner wear to baby wear has increased in the recent times. Due to this reason, a huge number of people were seen to be going to buy the products offered by Pacific Brands. As a result, the sales of the company were seen to be increasing. The company has key brands that include Sheridan, Bonds, Berlei and Jockey. As per the comparison between the annual reports of PWC of the first half of 2015 and 2016, it has been noticed that an 8.6% growth are there in the sales of all the major brands. KPMG reported that the EBIT was up around 14.9% and NPAT was up to 44.4% in all the operating groups (Cooney & Long, 2014).
Such growth was possible as Pacific Brands found plenty of labor force at cheaper rate and they had ample amount of capital in hand to invest for their business venture. The company was able to understand the requirement of the customers. Apart from that, the company have produced their products to fulfill their demands (Marks, 2013). The technology used in manufacturing the cloth in their factory was very much modernized and it led to produce the apparels, which are customized by the client requirements. The patents imposed by the government were also favorable in order to protect their manufacturing rights.
Political
The political factors in the clothing industry of Australia imply a complete support from the nation’s government. The nation imposes redefined import duties and tariff barriers which is very much effective for Pacific brands (Cooney & Long, 2014). The political stability, policy of the government, agreements regarding trade and the arrangements of taxation are favorable for the business of the company.
Economic
The current economic conditions in Australia indicate that the purchasing power of the Australian people is continuously increasing. The standard of living has also improved in a significant level. The strong demands for clothing and strong position of dollar at the global level have become very much favorable for Pacific Brands. The nation’s economic growth has a positive impact on the consumer’s income and savings level and it has enhanced their confidence to buy apparels of Pacific Brands (Nossar et al., 2015). The economic growth has also resulted to reduction of unemployment levels leading to more buying power of the consumers. The improved exchange rate has also a positive effect in the export of the company’s products.
If the social trends are properly analyzed, it will be noticed that the products, which are eco-friendly are highly preferred among the Australians. The demand for clothing across Australia actually states that people have the common taste to buy high quality products and it is strictly followed by Pacific Brands. The products Pacific Brands are fulfilling the religions and subcultures of the population in Australia (Rosenbaum-Elliott et al., 2015). As different country’s culture is different, the country can face difficulties in exporting the products due to lack of consumer preferences.
The trend of technology is also very important in the clothing industry and Pacific Garments is making a full utilization of the technology to achieve higher exposure in the industry. They are using modernized technologies in order to manufacture quality products for their clients and consumers (Cooney & Long, 2014). The company can use online shopping website for the distribution of their products. The online website provides enhanced opportunity to view the products for large number of customers both in the nation and all over the globe.
The climate and weather can have a significant impact in the company’s business. Australia, being the country of southern hemisphere, has the favorable climate for wearing the outfits of Pacific Brands (Pike & Bianchi, 2013). The change in climate can have a severe impact on the company’s business.
The Trade Practices Act enacted in the year 1974 and the international conventions and agreements are the important factors for a company’s business. If those act, conventions and agreements are favorable for the company then it can enhance its product distribution leading to increased profits (Sohaib & Kang, 2014). Such act and agreements are favorable for Pacific Garment’s business and have created opportunity for expansion.
Innerwear and baby wear represents one of the fastest growing clothing categories that have resulted in more competitors entering in the market. Here the competition type is monopolistic as the various competitors offer similar products while the competing brands approach for differentiating themselves from others (Bianchi & Birtwistle, 2012).
The main competitors of Pacific Brand are Zara, Benetton, Uniqlo, H&M and The Gap. They are all the direct competitors of the company.
| Name of the competitor | Percentage of global share | Growth Trend | Competitive Advantages |
| H & M | 1.6 | They have expanded globally in the developed and emerging markets. | They have high brand strength. They have partnerships with the luxury designers. |
| Zara | 1.4 | They have grown their business to China, Japan and South Korea as well as in Italy, France, UK and Germany. | They have a sophisticated network of feedback, low advertising expenses and fast creation cycle. |
| Uniqlo | 0.7 | They have mainly grown their business in Hong Kong, China and Taiwan. | They have high tech innovation system and a low cost model (Marks, 2013). |
| The Gap | 1.4 | They have developed franchise stores in the top ten clothing markets in the world. They have also entered in Western Europe and China. | They have a growing online division, which has enhanced their customer base. |
| Benetton | 0.2 | The company has a significant growth in the European Countries as they are majorly concentrated towards European market. | They produce the basic styles of apparels in varieties of colors. The company is also vertically integrated. |
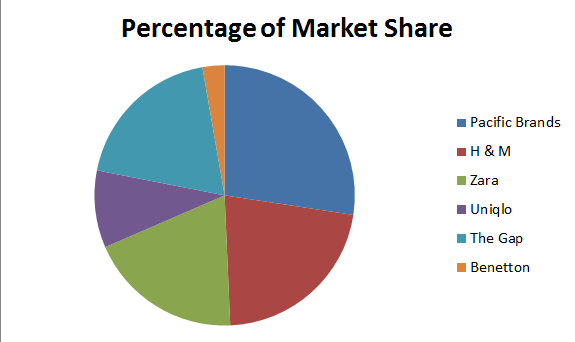
Market Share of Pacific Brands and its competitors
Source: (Marks, 2013, Pg-574-575)
Similarities and Dissimilarities of the competitors with Pacific Brand
| Competitor Name | Similarities | Dissimilarities |
| H & M | Expansion in the global and emerging markets. | Pacific Brands don’t have partnerships with luxury designers. |
| Zara | Fast creation cycle and growth of business in China, Japan as well as Italy and France. | Pacific Brands advertising expenses are high. |
| Uniqlo | High Tech Innovation system. | Pacific Brands does not have low cost model as their advertising expenses are high (Cooney & Long, 2014). |
| The Gap | Development of franchise stores in top ten apparel markets. | The online division of Pacific Brands is not flexible. |
| Benetton | Production of basic styles of apparels in varieties of colors. | Pacific Brands have focused not only in European countries but also in Asian countries for business expansion. |
Pacific Brands has the advantage for getting finance resources from the reputed banks in Australia. They can get plenty of skilled employees at cheaper rates. Moreover, its headquarters is located at Melbourne and its retail outlets are located in the major cities of Australia like Sydney, Perth, Canberra and Adelaide (Jagel et al., 2012). Such cities are the big market of the products they deal with.
The company’s improved service quality in its distribution, proper positioning of its product for its target market, sufficient number of effective resources such as manpower, money, and materials has given an enormous competitive advantage to it over others (Weller, 2013). The company’s geographical location and a high potential in delivering quality products has led it to be the market leader.
The target market can be segmented based on demography, lifestyle and behavior of the customers. It will be single target market where the customers will be of innerwear, socks, baby wear and outwear. The market will be huge as the products are considered essential for common people (Sohaib & Kang, 2014). The target market will be the people of Australia and the products will be launched keeping in mind of the demographic and lifestyle changes. The target market will be people from 25 to 50 years of age.
The innerwear itself is a convenient product with a mass-market appeal. It has targeted individuals of all class and all age groups. However, the primary market is the 25-50 age groups residing in the metropolitan areas of Australia. As per the ABS census data, about 5 million populations were aged between 25 and 50 years by the end of 2014 (ABS, 2015).
Considering the segments of lifestyle, the people of that age group are highly suited to be the target market. Those people are cultured, mostly married, renting flat in the major metropolitan cities living with their families. They have a healthy income and due to this reason they are not price sensitive. They are the energetic individuals who are enthusiastic of getting a comfortable wear.
The SWOT analysis of Pacific Brands has been given below,
Strengths
Weaknesses
From the above discussions, it can be stated that though Pacific Brands has got a significant position in the clothing industry, they have a large way to go for maintaining their competitive position. They have to build a low cost structure model and have to improve their online business technologies so that it can make a positive impact on their customer base. If they follow the path through implementation of innovative strategies by proper utilization of their available resources, in the near future they will be the ultimate name in the world of clothing.
Australian Bureau of Statistics (2015), Australian Demographic Statistics Tabels, retrieved 11 November 2015 from http://www.abs.gov.au/AUSSTATS/abs@.nsf/DetailsPage/3101.0Mar%202015?OpenDocument.
Bianchi, C., & Birtwistle, G. (2012). Consumer clothing disposal behaviour: a comparative study. International journal of consumer studies, 36(3), 335-341.
Cooney, R., & Long, M. (2014). Market coordination and training networks in Australia. Economic and Industrial Democracy, 35(4), 609-627.
Home » Pacific Brands. (2016). Pacificbrands.com.au. Retrieved 5 August 2016, from http://www.pacificbrands.com.au/
Jagel, T., Keeling, K., Reppel, A., & Gruber, T. (2012). Individual values and motivational complexities in ethical clothing consumption: A means-end approach. Journal of Marketing Management, 28(3-4), 373-396.
Marks, A. (2013). The Globalization of the Australian Textile, Clothing, Footwear and Motor Vehicle Industries: Results in Line with Other Western Market Economies. Global Economy Journal, 13(1), 129-150.
Nossar, I., Johnstone, R., Macklin, A., & Rawling, M. (2015). Protective legal regulation for home-based workers in Australian textile, clothing and footwear supply chains. Journal of Industrial Relations, 57(4), 585-603.
Pike, S., & Bianchi, C. (2013). Destination brand equity for Australia: Testing a model of CBBE in Short-Haul and Long-Haul Markets. Journal of Hospitality & Tourism Research, 1096348013491604.
Rosenbaum-Elliott, R., Percy, L., Elliott, R. H., & Pervan, S. (2015).Strategic brand management. Oxford University Press, USA.
Sohaib, O., & Kang, K. (2014). Cultural Aspects of Business-to-Consumer (B2C) E-commerce: A Comparative Analysis of Pakistan and Australia. The Electronic Journal of Information Systems in Developing Countries, 61.
Weller, S. (2013). Consuming the city: Public fashion festivals and the participatory economies of urban spaces in Melbourne, Australia. Urban Studies, 50(14), 2853-2868.
Upload your Assignment and improve Your Grade
Boost Grades